A Beginner’s Guide to Keyword Research
What you’re reading is a step-by-step guide that will help you conduct effective Keyword Research. In this way, you will improve your SEO rankings and attract more quality traffic to your using the SEO Tester Online Keyword Explorer Tool.
What is Keyword Research?
Keyword Research is the activity of searching and analyzing the keywords that users look for on search engines (such as Google, Bing, Yahoo, or Amazon) to answer a question or to solve a problem.
It plays a vital role in your SEO strategy, and it can help you rank among the top results within the SERP.
Why is Keyword Research important?
Keyword Research is useful to find new topics to cover in your articles or products to sell on your website. It allows you to more scrupulously analyze your competitors and optimize conversions in your Google Ads campaigns.
Choosing the right keywords allows you to learn about your potential users and understand what they are looking for, allowing you to write useful and relevant content compared to your searches.
Also, it will help you write all the content you need, such as email, Facebook Ads, and Social Media.
Three Essential Concepts for Keyword Research
Before you start your first Keyword Research, there are three basic concepts you should know:
- Search Intent
- Search Volume
- Keyword Difficulty
Search Intent
Search intent refers to the goal that a specific search has, which is why a user looks for something on the search engine.
There are five types of search intent:
- Informational: when the goal is to know-how. These searches have high volumes but a low traffic value. In fact, the user searches for information on a particular topic or product, but it is not said that he will be willing to acquire it.
An example of information research is: “What is Crossfit?”
- Navigational: the goal is to reach a website or brand that the user already knows. These searches have medium-high traffic value and volume.
An example of navigational research is: “Nike shoe site.”
- Transactional: the user is willing to buy a product or service. Queries with this intent have a very high traffic value because the user is ready to purchase and the conversion closer.
An example of transactional research is: “Nike Air Force 1 price”.
- Commercial: Similar to the previous research intent, it is characterized by an interest in a category of products or services. It is a search not directly aimed at immediate purchase.
An example of commercial research is: “Best running shoes.”
- Local: refers to research that aims to research local activities with physical presence such as restaurants, hotels, shops, professional studios, and many other similar types of business. No less than 20% of search queries have local intent.
Example of a search with local intent: “Gyms in Milan.”
If you have any kind of business with a physical location, have a look at our local SEO blog section.
Search Volume
That’s the average number of monthly searches performed in a country over 12 months. It is a useful metric for estimating potential traffic for a specific keyword.
The higher the volumes of a particular keyword, the more traffic you can get from it.
Also, the higher the search volume of a keyword, the greater the effort required to rank high within the SERP.
However, remember that search volume is not the only piece of data to consider when you look for ranking opportunities.
Not always a highly searched keyword is the right one. Think of all those queries with informational search intent.
On the other hand, you should think twice before discarding a keyword with a medium-low search volume (500-999 monthly searches).
You also need to consider other factors, including:
- Type of your business;
- Size and importance of your niche;
- Search intent;
- Keyword Difficulty.
Keyword Difficulty
Shows the difficulty of ranking in the top 10 results for a given keyword.
When it comes to Keyword Research, KD is a relevant factor in organic research.
Keyword Difficulty takes into account several factors, such as the authority of well-ranked websites and their backlink profile.
It’s useful to know the difference between 2 particular types of keywords:
- Short-tail keyword: usually formed by one or two words, they represent a generic search query;
- Long-tail keyword: They are more specific search phrases, with lower search volumes than short-tail keywords.
Long-tail keywords have lower search volumes but also answer to more specific needs. For this reason, they are considered less competitive but also more profitable.
Read our guide on how to find long-tail keywords related to your niche.
With these three basic concepts, we can now focus on the best way to do Keyword Research using the Keyword Explorer Tool.
How to make an outstanding Keyword Research
Ask yourself the right questions
To search for keywords for your customers or your project, you must first ask questions, which will help you clarify the current situation of your business and better understand your niche.
Create a new text file or get a regular notebook and pin the answers to these seven questions:
- Who does your business speak to?
- Who is your ideal customer?
- Which problem do you solve?
- Who are your competitors?
- What do they write about, and how they do it?
- What makes you unique compared to your competitors?
- What is the goal of your website?
These questions allow you to have a more linear view of the entire project, and by answering them, you will create a brief. A brief is a document that will guide you in the keyword search and in creating content for your site from an SEO perspective.
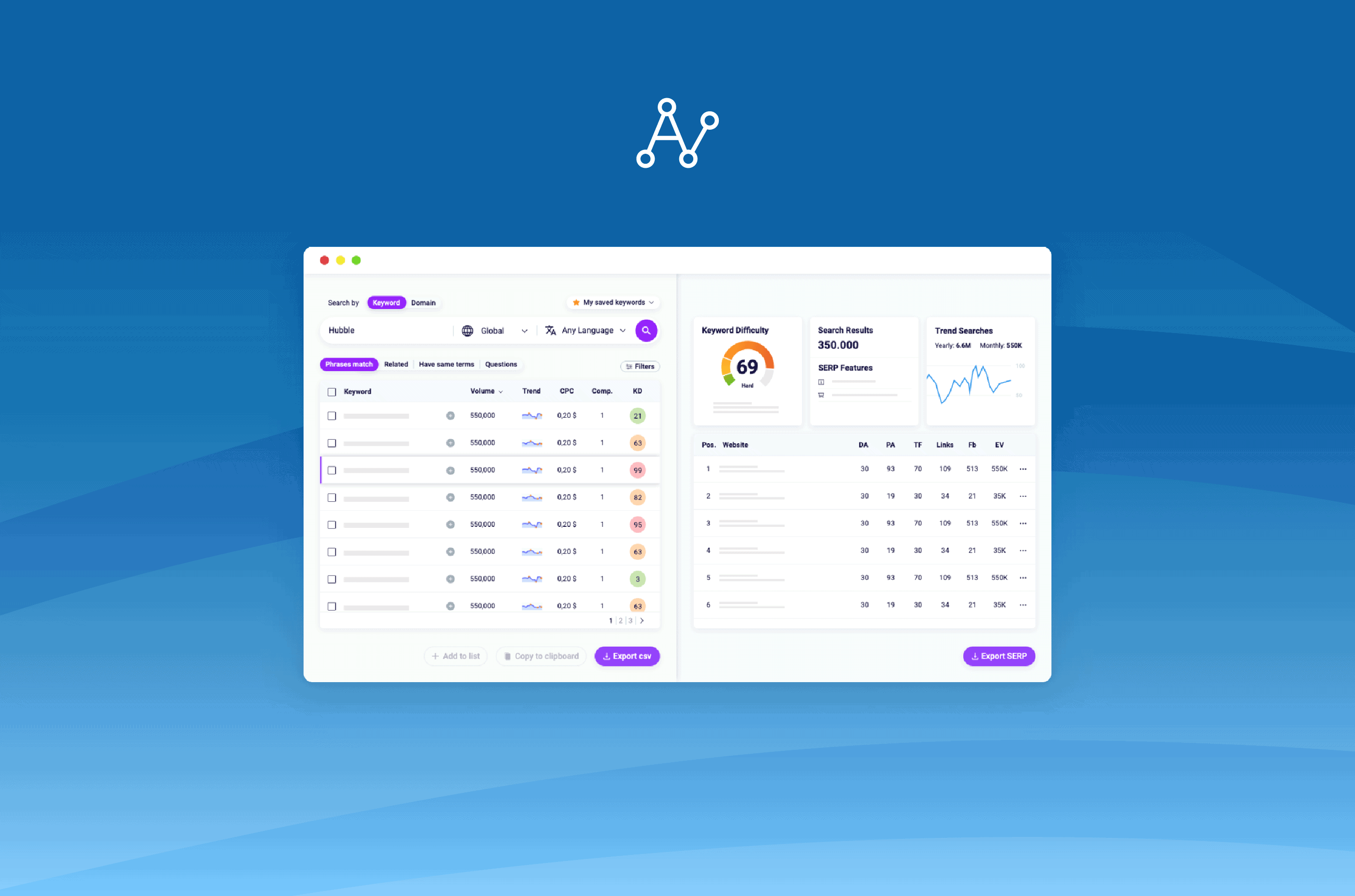
Keyword Research with Keyword Explorer Tool
Now that you have a clear picture of the basics of Keyword Research and you know what the questions are, you can start!
Generate Keyword ideas
First of all, sign in to the Keyword Explorer Tool.
Don’t worry if you haven’t subscribed to any of the SEO Tester Online plans. You can still use it for free a limited number of times every day.
As you can see, you have the option to start your search from a keyword or a domain.
Which one to start with?
If you just started, and you absolutely know what the most critical keywords in your market are, domain search is the best way to find out the keywords your competitors are positioning for.
So, for example, if you’re managing an e-commerce website that sells sports shoes or, more generally, sportswear, you can write the URL of your competitor’s site and press the button to start the search.
Within seconds, you’ll get a list of the most essential keywords your competitor is ranking with. That’s great, isn’t it?
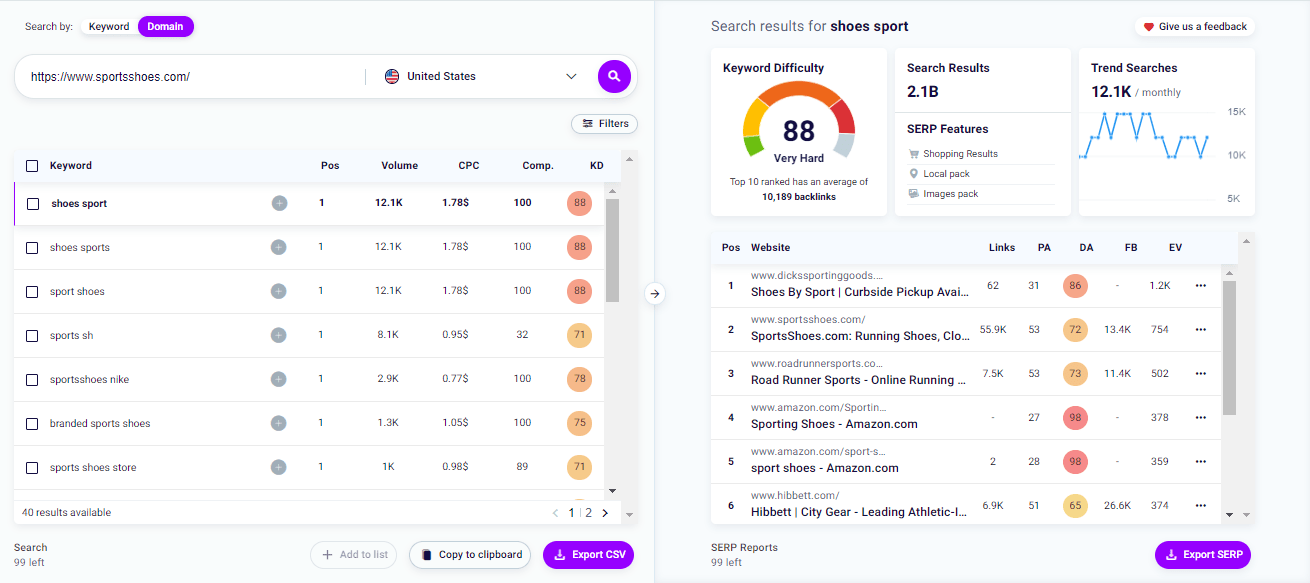
If you already know the main keywords of your website, and you are looking for tips and new insights based on the key metrics of the keyword research, we recommend that you start with a keyword search.
To start, choose a short-tail keyword that identifies one of the topics covered by your site, select the country, and click on the search button 🔍.
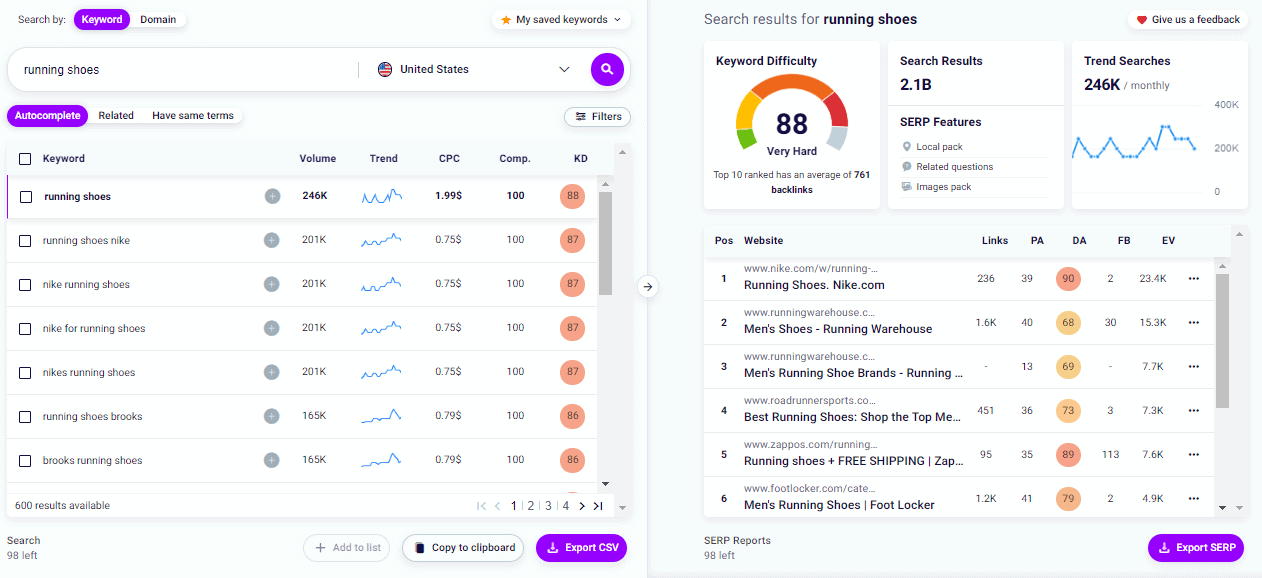
On the left, the Keyword Explorer Tool will show a list of keywords and metrics that will allow you to identify new placement opportunities.
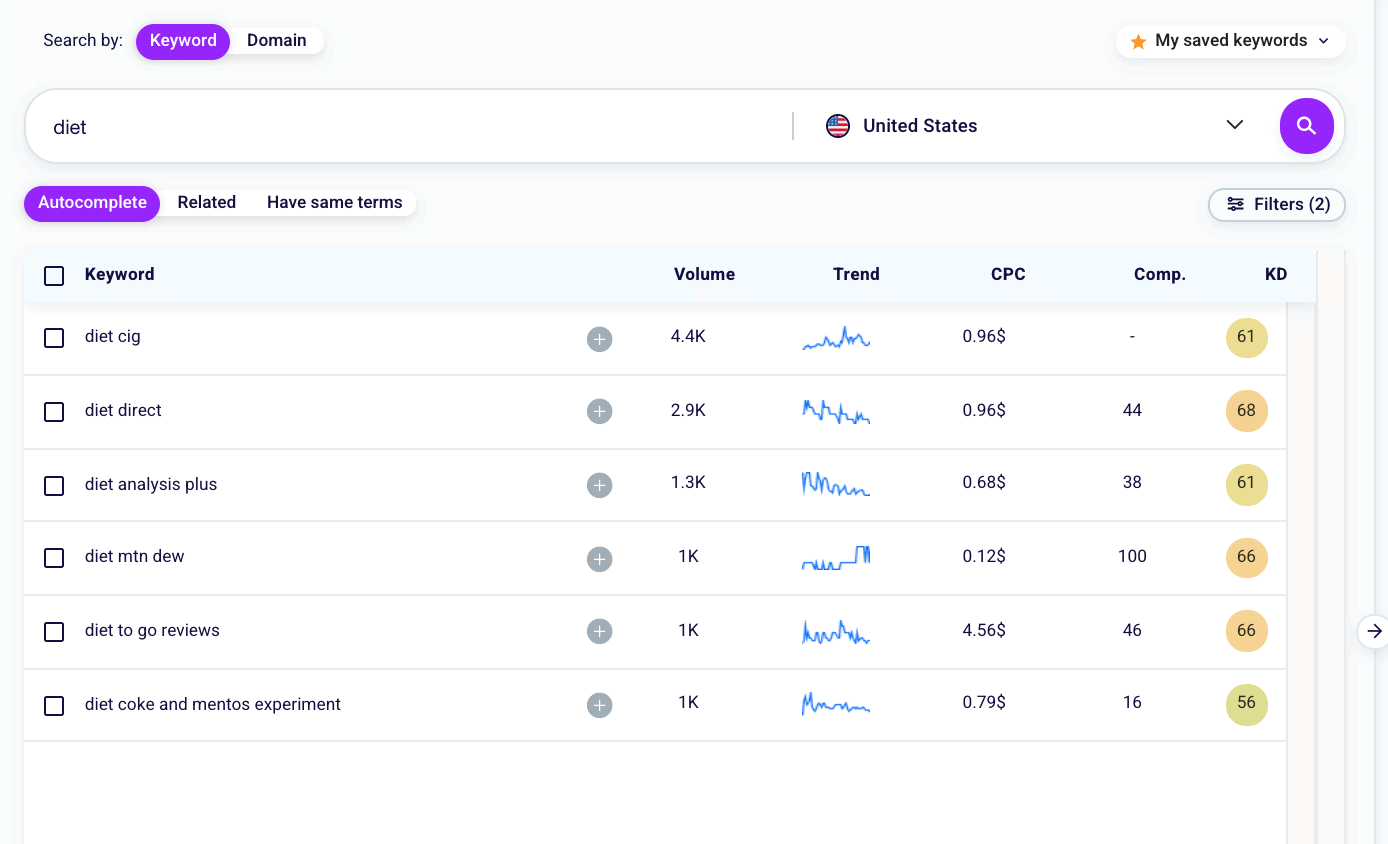
Besides the search volume and keyword difficulty, you’ll find three more metrics:
- Trend
Indicates how much the user’s interest in a given search has varied over the past 12 months.
This is useful if you have a seasonal or holiday-based business.
- Cost per Click (CPC)
It’s the estimated offer in Google Ads for a given keyword.
In other words, it’s the average price the advertiser has to pay for every click on a paid ad.
- Competition
It is the level of competition for a given keyword in the Pay-Per-Click (PPC) campaigns.
A higher level of competition results in a higher CPC for that keyword.
Filter your searches
With the Keyword Explorer Tool, you can further generate new keyword ideas using the functions:
- Related Searches
- Equal Terms
Related keywords are associated with the main keyword (the one you searched for) and are beneficial for intercepting potential users with similar needs.
Related research is defined as:
- Synonyms;
- Grammatical variations;
- Questions;
- Long-tail keywords related to the main one.
Imagine having e-commerce that deals with sneakers. The main keyword “sneakers” will likely have related searches such as “girl sneakers” or “men’s sneakers on sale” or “tennis shoes.”
Thanks to our tool, you can search for keywords through the use of different filters. They come in handy and will help you get even more accurate results.
You can decide whether to show results that include or exclude a particular word, set the minimum or maximum search volume to your liking, and also determine the values that interest you most in Competition, Cost per Click, and Keyword Difficulty.
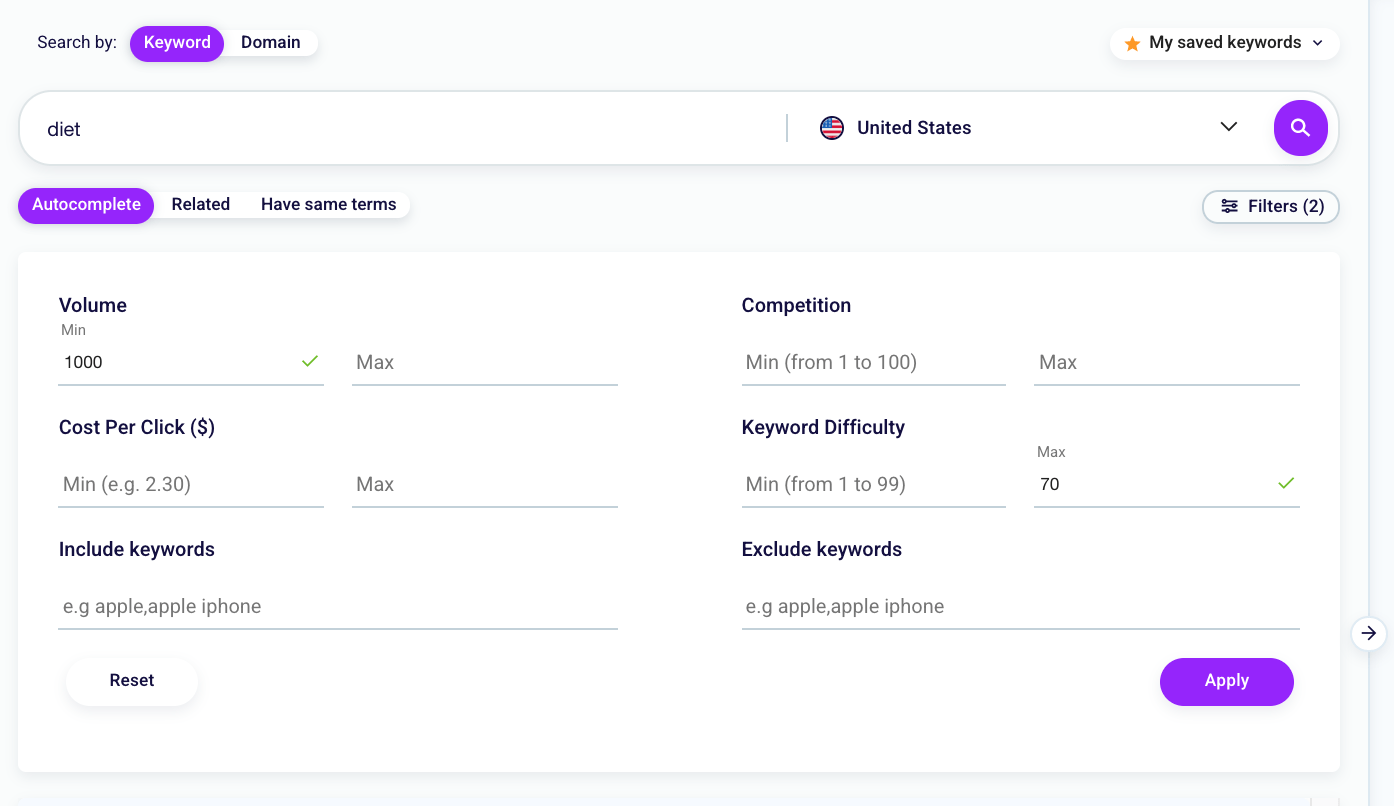
Imagine you’re running a blog about nutrition; for the “diet” query. Set a Maximum Keyword Difficulty of 70 and a Minimum Search Volume of 1000, as in the screen below. Now, sort the keywords by KD to choose the ones that are right for you.
Create the Keyword List
Now, it’s time to create a keyword list.
This will allow you to have them under control all the time.
If you are starting a new project, create a separate list that includes all the main keywords for your business.
It takes two clicks to create a new list.
Click on “My Keywords” When the window opens, click on “Create your list.”
Search for keywords related to your business again and filter them. Click on the checkbox to the left of each keyword. There, you can add the keyword to your list by clicking on “Add in List.” You can also click on the button to the right of each keyword.
Once you’ve created your list, you can view it by clicking on “My Keywords” and then on 🔍.
Have you saved the keywords you’re most interested in? Don’t forget to export the results and your list to CSV!